A Comprehensive List of Drugs That Raise Blood Sugar Levels
However, carb-rich diets aren’t the only cause of rising blood sugar levels. Other factors contribute to spikes in blood glucose; a major one flagged by professionals is drug intake.
You might wonder how this is so. Aren’t drugs meant to contribute to healthier living and help manage a particular condition? While this is true, they sometimes contribute to increased blood sugar levels in many ways.
In this piece, you’ll discover the key drugs that can raise blood sugar, how to measure blood sugar levels, how to manage high blood sugar, and more.
What to Expect
- What Do Blood Glucose Levels Mean?
- What Is Drug-Induced Diabetes?
- Drugs That Contribute to a Blood Sugar Spike
- Signs You Have High Blood Sugar
- Testing Blood Sugar Levels at Home
- How to Manage Blood Sugar Level
- Emergency Care For Hyperglycemia
What Do Blood Glucose Levels Mean?

Diabetes is a health condition closely tied to blood sugar levels. Naturally, the body uses glucose as fuel, mainly from carbohydrates-rich foods. In addition, the body burns glucose to supply the organs with energy, and the hormone insulin aids this process by transporting glucose into the blood. Excess glucose from this process is usually stored in the liver and muscles for future use.
However, sugar accumulates in the blood when the body can’t produce or use insulin properly. This leads to a condition known as hyperglycemia, which is when there’s too much sugar in the blood.
The body’s inability to process sugar at this point exposes it to many risks and complications. For example, you likely have high blood sugar if you experience excessive thirst or hunger, vomiting, and vision problems.
When not properly managed, hyperglycemia ultimately leads to diabetes. People predisposed to diabetes are at greater risk of developing the illness if they don’t maintain an average blood glucose level. Several tests help determine if a person has diabetes or not; a prominent one is the blood glucose test.
According to the CDC, a fasting blood sugar test that reads a blood sugar level of 100 mg/dL is normal; one that reads between 100 to 125 mg/dL indicates prediabetes, and that which is greater than 125 mg/dL indicates diabetes.
Many diabetes treatments aim to reduce blood sugar and help the body better utilize insulin. Hence, watching out for a diet that can lead to blood sugar spikes and eliminating certain unhealthy habits is crucial. However, apart from what you eat, other factors contribute to high blood sugar. Some medications have also been observed to affect blood sugar levels, as we’ll see soon.
What Is Drug-Induced Diabetes?

Diabetes can occur based on genetic conditions, usually aided by external factors like environment or eating habits. However, diabetes can also result from other factors that many don’t consider. One of these is drugs.
Drugs help in fighting illness and restoring the body’s health to normal. However, some drugs have been observed to influence the development of diabetes in some patients. Drug-induced diabetes is not uncommon and can arise when using certain medications.
Fortunately, drug-induced diabetes is often reversible, especially when caught early and the medication discontinued. However, it can become permanent in some patients.
While you can afford to stop certain medications, some other medicines are just too essential to discontinue. Hence, it’s important to know which drugs can contribute to the development of diabetes and how to manage them properly.
Usually, these drugs affect blood glucose levels negatively, often leading to spikes in blood sugar. In some cases, these drugs influence how the body reacts to insulin and sometimes result in insulin resistance. These include diabetes, over-the-counter prescription, blood pressure, mental health, and other medications.
While you can’t avoid using some medicines, a healthy diet and regular exercise can help you better manage blood glucose levels.
Drugs That Contribute to a Blood Sugar Spike
Knowing the drugs that can potentially raise blood glucose levels can be tricky. They can even be drugs prescribed to you by your doctor. However, below are some drugs that can increase blood sugar levels.
(N.B: Some of these drugs can also cause low blood sugar).
Steroids
Steroids effectively treat conditions like arthritis, asthma, inflammations, allergies, and more. It also helps deal with autoimmune disorders and suppresses the immune system to prevent tissue damage during organ transplants. However, some steroids like prednisone significantly affect blood sugar and can eventually lead to diabetes.
Typically, steroids can make the liver less responsive to insulin after usage. The liver is the storehouse for glucose the body uses when it runs low. As your body needs glucose, the liver releases a certain amount to serve this need.
If, however, there’s enough blood glucose present, the pancreas secretes insulin to control the body’s sugar level by triggering the liver to stop glucose release. When insulin is unable to perform this function, it leads to a blood sugar spike, which can potentially be dangerous.
Diabetes is often a result of the body’s inability to make use of or produce insulin, often resulting in either type 1 or type 2 diabetes. A prolonged inability for the body to properly use insulin in people that use steroids leads to insulin resistance. This is when the body stops responding to insulin even when injected into the system. At this point, a condition known as steroid-induced diabetes is said to manifest.
Steroid-induced diabetes is observed to behave a lot like type 2 diabetes, and if not properly managed, it can eventually lead to it. However, while type 1 and type 2 diabetes are lifelong ailments, steroid-induced diabetes will resolve following the completion or cessation of steroid treatment.
Taking steroids for a more extended period (3 months or more) increases one’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This risk is even higher in people predisposed to this condition or diagnosed with prediabetes. In addition, other side effects like muscle weakness, hypertension, mood swings, etc., come with its use.
Common steroids to watch out for are hydrocortisone and prednisone. Luckily, steroid skin creams (for rashes) and inhalers (for asthma) don’t pose a significant risk.
Antipsychotics
Over 900 million people worldwide currently experience mental illness. To put things into perspective, that is 1 in 8 people.
Meaning quite a lot of people have to deal with a mental disorder episode during their lives. In the US, 3% of the population experience at least one psychotic episode each year, most of which occur during early adulthood. While most psychosis cases arise due to this disorder, many can also be linked to sleep deprivation, substance use, stress, etc.
Many people with this illness receive antipsychotic treatment to help them manage their condition. However, studies have shown that these medications do have a significant impact on blood sugar.
Antipsychotics came into play about 72 years ago and have since proven effective in helping people with severe mental illness manage their condition. Scientists have long since observed a trend of people with this illness developing diabetes down the line. Although the reason for this has been claimed to be multifactorial, recent research has linked it to antipsychotic use.
A review titled “Association Between Antipsychotic Medication Use and Diabetes” points out that higher doses of antipsychotics are associated with an increased risk of developing diabetes and diabetes complications. In addition, according to this review, taking these drugs can potentially lead to weight gain, which is one of the risk factors for diabetes.
Another study explored the relationship between antipsychotics and diabetes. It found that children and youths who use antipsychotic treatment for mental illnesses like schizophrenia are at more risk of developing diabetes when they take these medications in cumulative doses.
Also, it states adults aren’t exempted from this risk as they can also develop type 2 diabetes after using these medications for a prolonged period. It further points out some of the metabolic effects of antipsychotics, including weight gain, insulin resistance, and increased glucose levels.
Statins
Cardiovascular problems aren’t uncommon in people with diabetes; for one, having diabetes increases the risk of developing heart disease or stroke. Also, you stand the chance of cardiovascular issues if you have too much LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol) in your system, regardless of if you have diabetes or not. Hence, one of the primary ways to tackle this problem is to reduce the amount of bad cholesterol you consume and up the intake of “good” ones (HDL).
Although you can rely on food sources for “good” cholesterol and avoid some diets to reduce LDL cholesterol, there are medications called statins, proven effective in reducing the amount of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in the body.
Depending on your level of diabetes, you should take a moderate or high-intensity statin to prevent further complications. The American Diabetes Association advises people over age 40 living with diabetes to opt for moderate potency statins.
A 2016 review established the link between blood sugar levels and statins. It was observed that this medication unfavorably affects blood glucose levels in diabetes patients. Another 2016 review corroborated this research, observing statins to increase blood sugar and ultimately increase the risk of developing diabetes.
Other researchers linked higher doses of statins to an increased risk of developing diabetes. For those already living with diabetes, this drug can potentially increase their blood sugar to a dangerous level. In addition, statins can cause health hazards instead of preventing them when not adequately monitored.
However, not all statins are bad eggs; there exist certain statins that rarely affect blood sugar, hence posing the lowest risk of elevated blood glucose levels (e.g., lovastatin and pravastatin). Some of these drugs aid blood glucose control in some cases. Still, more research needs to be carried out.
Despite the harm statins pose, they’re too crucial for cardiovascular health to be abandoned. Hence, the FDA recommends its usage regardless.
Antihypertensive drugs
About 47% of the adult population in the United States have hypertension with a blood pressure reading greater than 130/80 mmHg. Worldwide, about 26% of the population lives with hypertension.
Considering these statistics, the growing prevalence of hypertension is quite glaring. High blood pressure can still lead to various complications, including heart attack, stroke, kidney disease or failure, vision loss, etc.
Hypertension can occur in anyone, whether they have a preexisting condition or not. Thankfully, antihypertensive drugs containing agents like beta-blockers and diuretics help manage the condition. You can safely live with hypertension for a long time if adequately managed without fearing complications.
However, studies have shown these drugs can negatively affect blood glucose levels. For example, this research on “Antihypertensive Drugs and Glucose Metabolism” observed that medications like beta-blockers and diuretics are more likely to have disastrous effects on blood glucose which can lead to complications like cardiovascular diseases or diabetes. It also states that people living with hypertension also might experience insulin resistance which can contribute to the build-up of sugar in the body.
Birth Control Pills
Birth control pills and other contraceptives have proven effective in preventing unwanted pregnancy. For women with diabetes, patches, implants, pills, injections, and rings have been checked to be safe options. However, it’s no news that some present specific side effects when used.
Several researchers have looked into the relationship between diabetes and birth control methods. For example, some claimed that estrogen in birth control pills could cause insulin resistance in some patients, eventually leading to blood sugar spikes. In contrast, others didn’t find variation in blood glucose levels in women with diabetes taking birth control pills.
However, we can’t overrule the findings of this research. Hence, physicians often recommend birth control pills with the minimum estrogen level for women with diabetes. At the same time, some physicians avoid prescribing birth control pills to women living with diabetes.
Furthermore, other researchers have linked birth control pills to some diabetic complications, especially when taken for over two years.
Antibiotics
People with diabetes often need antibiotics due to various infections resulting from this condition. However, some antibiotics have been observed to cause insulin resistance, increasing blood sugar levels.
More particularly, a class of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones has been observed to cause high and low blood sugar. The antimicrobial drug (pentamidine) also has the potential to raise blood sugar.
Signs You Have High Blood Sugar

Your body has a way of naturally informing you when something is wrong with it. It does this by showing specific symptoms that won’t surface unless there’s a problem. Hence, you must pay attention to your body’s subtlest signs.
For example, when faced with hyperglycemia, the body provides several warning symptoms to alert you of this problem. So, here are some signs you’ll experience if your blood sugar levels are over the chart.
Earlier on, you might start to experience the following:
- Extreme thirst or hunger
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Numb feet
- Frequent urination
- Weight loss
- Skin infections
Extreme symptoms include:
- Vomiting
- Dehydration
- Rapid heartbeat
- Confusion and disorientation
- Fruity smell of the breath
- Labored breathing
- Coma
If you experience any of the above symptoms, there’s the possibility you’re experiencing high blood sugar levels. You should check it out with your doctor to know for sure or perform blood sugar tests to figure this out for yourself.
However, if you start having extreme symptoms like fruity-smelling breath or vomiting, visit the nearest emergency room; you might be suffering from a condition known as ketoacidosis.
Testing Blood Sugar Levels at Home
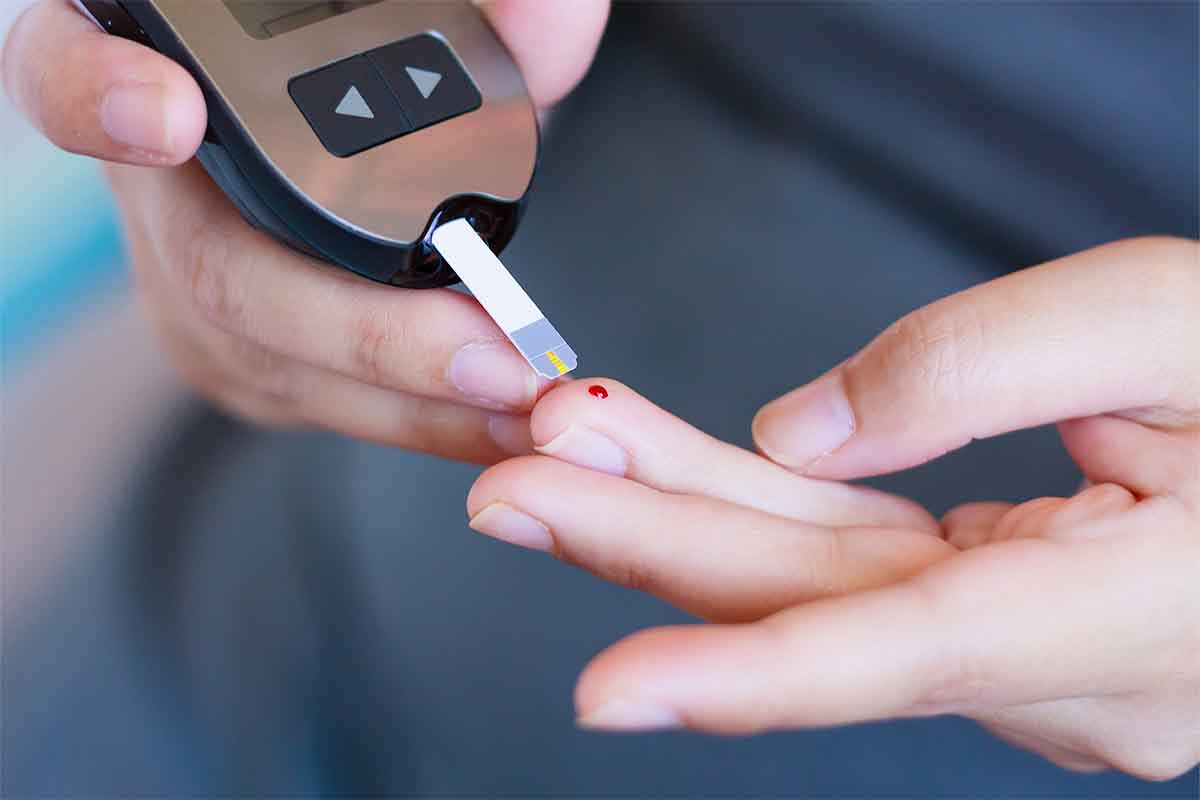
It’s a good idea to regularly check your blood sugar level, even when you’re not experiencing any of the symptoms above. Luckily, you don’t need to see your doctor or go to the nearest emergency room to get this done. Instead, you can easily check your blood sugar in the comfort of your home. Here are some ways you can do this:
Home Glucose Monitoring
Using a blood sugar meter, you can easily measure your sugar level. All you need is to follow these simple steps:
- Wash and dry your hands
- Using the lancet, prick the side of your finger
- Massage until blood appears, then put a drop of blood on the test strip
- Place the strip back into the meter
The meter will process your blood and display your blood sugar levels, after which you can go ahead and record the result.
Other types of meters allow you to test different parts of your body. For instance, you can test your forearm, thigh, or the base of your thumb. However, results from these kinds of meters tend to differ from that of a fingertip stick. Also, depending on the type of meter, you can get an average of your blood sugar levels over time or even access software that helps you better monitor this information.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
With this system, you can also measure your blood sugar level. Although it’s not as accurate as the method cited above, it can easily find patterns in your blood sugar levels.
It works by attaching a tiny sensor under the skin that monitors blood sugar levels every 5 minutes. This information is relayed to a monitor where you can access the details. Using this device’s cumulated information monitored over time, your doctor can spot trends in how your blood sugar ranges. However, this method shouldn’t replace regular blood sugar checks.
How to Manage Blood Sugar Level

You can get your blood sugar level to stay within the normal range. This way, you can avoid complications that can come with high blood sugar. Here are some ways to manage your blood sugar:
Exercise
Physical exercise is one of the best ways to maintain that optimum blood sugar level. Therefore, people with diabetes are advised to get regular exercise. It not only helps control blood sugar, but you also get to shed excess weight that may be a risk factor for developing further complications.
However, avoid exercising when experiencing conditions like ketoacidosis (elevated ketone levels). Exercising in this state can further raise the blood sugar level.
Follow Proper Diet
Eating healthy is another way to ensure your blood sugar doesn’t go off the chart. There are unique diabetes diet plans specially created for people with diabetes. They’ll help better manage your condition and prevent spikes in blood sugar.
Avoid sugary beverages and frequent snacking. Also, ensure you stick to a particular meal plan. You can contact your doctor or dietitian to determine which meal plan is the best for you.
Check Your Blood Sugar Often
There’s no better way to get ahead of hyperglycemia than doing frequent blood sugar checks. That’ll give you a real-time update on your blood sugar level.
You can follow the earlier steps to check your blood sugar from home. Then, visit your doctor if you notice spikes in your blood sugar.
Adjust Your Insulin Doses
You might experience blood sugar spikes if you’re not taking the proper insulin doses. However, sometimes you need an extra amount to manage high blood sugar. You should check with your doctor to know when to up your doses to correct a high blood sugar level.
Take Your Medications Properly
Often, complications arise when you don’t take your prescription medicines correctly. Usually, taking too little or too much of a particular medication will significantly impact how they work and the kind of side effects they present. So, ensure you take your diabetes medicines as prescribed by your doctor.
Emergency Care For Hyperglycemia

In case of severe hyperglycemia (which can result in diabetic ketoacidosis), you’ll need more than just exercise. Diabetic ketoacidosis is an acute medical condition resulting from too many ketones and sugar in the body. This condition can be life-threatening. Treatment includes:
Fluid Replacement
One of the symptoms of hyperglycemia is frequent urination. Hence, you’ll need to compensate for lost fluids by receiving fluids through your veins. The fluids will rehydrate you and help dilute excess sugar in the blood.
Electrolyte Replacement
Just like fluids, your body also loses several electrolytes due to the absence of insulin. These electrolytes are essential for the proper function of your tissues. For example, electrolytes are passed through your veins, ensuring your muscles, nerve cells, and heart function optimally.
Insulin Therapy
Ketoacidosis usually results from insufficient insulin to properly process sugar in your system. Therefore, you’ll need insulin to help manage this condition. Also, insulin reverses the build-up of ketones in the blood.
Summary

High blood sugar raises lots of concerns for people with diabetes. It often occurs due to the body’s inability to utilize the insulin hormone for processing blood glucose.
However, this guide taught you that certain medications can also increase blood sugar levels. These include but aren’t limited to diabetes, blood pressure, and mental health medications. These medications have been observed to influence insulin secretion, causing insulin resistance which can, in turn, lead to drug-induced diabetes.
You might not be able to avoid taking these medications. However, ensure you maintain healthy living by exercising regularly, following the right meal plan, and taking your medications correctly.
Our diabetes management app, can further aid you in adopting a healthy diet plan. It has all you need regarding the proper diabetes meal plans and exercise routines. This app can also help you monitor your blood glucose levels. However, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider for proper guidance.